Oracle EBS Implementation
Customer: Harsco Environmental
Date: Feb 2023 – Feb 2024
Location: Bizkaia, Spain
Metodology: Scrum
Role: Project Manager
Team Size: 6
The Project
Oracle Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) offers solutions for enterprise resource planning, aiding organizations in managing their financial operations, supply chains, and other key aspects in an integrated manner.
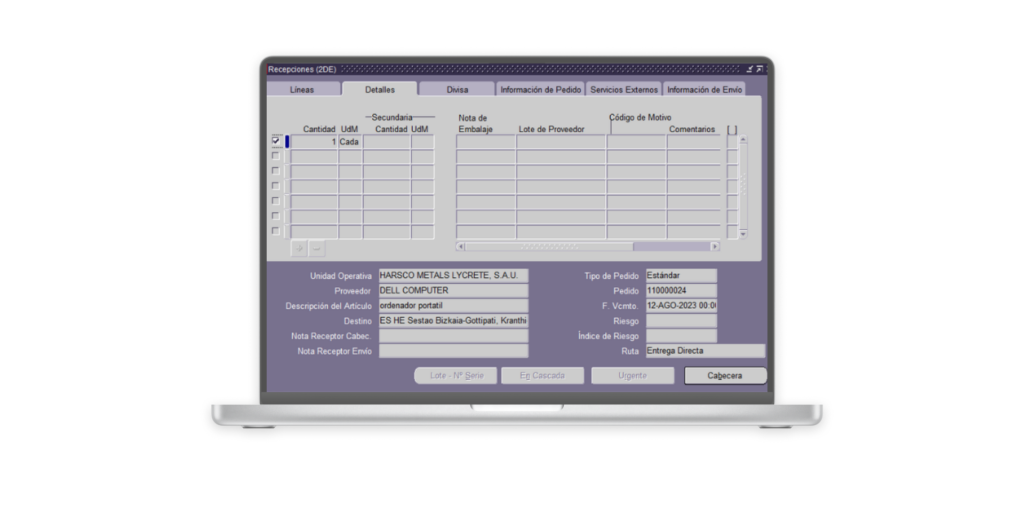
Scope: Implementing Oracle across workplaces in Spain and Portugal, covering critical areas for the company’s functioning such as Procurement, Finance, Sales, Purchase Order Generation, and Receipt. The goal was to enhance operational efficiency, system integration, and optimize business processes.
The software was implemented for 4 main departments
01- Finance
Optimization of economic data management, enhancing accounting, invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting. Oracle enabled greater control over income and expenses, more effective financial planning, and informed decision-making.
02- Buyers
Enhancement of procurement management, allowing more effective tracking of suppliers, orders, price comparison, and inventory management.
03- Site Managers
Oracle played a pivotal role in enhancing sales management, order tracking, and work order generation, thereby achieving greater operational efficiency at workplaces and significantly reducing delays and issues in the supply chain.
04- Site Admins
Oracle streamlined order management, inventory, and transaction coordination, ensuring smooth logistical flow and efficient coordination among departments.
ABOUT
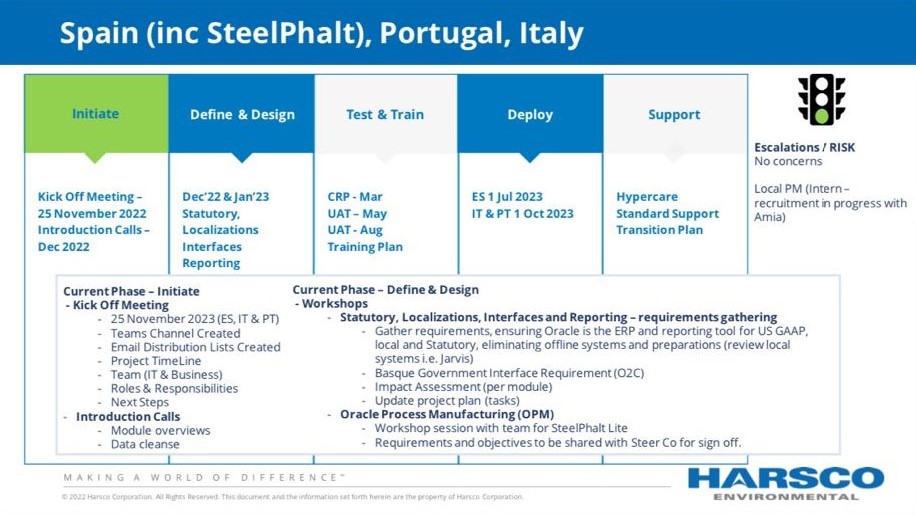
Project Phases
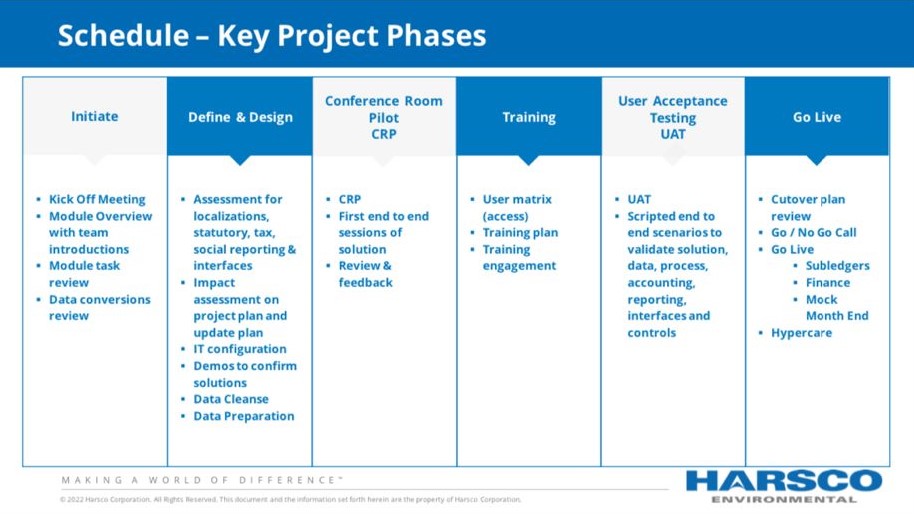
The project was structured into seven key phases spanning from inception to full operability and support. These phases represented pivotal milestones in the effective integration of Oracle’s enterprise solution. Each stage delineated a path starting from initial planning and culminating in system implementation and ongoing maintenance. Within each phase, specific activities took place, ranging from assessment and design to data migration, configuration, thorough testing, and the final transition to the operational environment.
The following slides provide a detailed visual representation of each stage, offering a clear and comprehensive understanding of the implementation process.
Here are the key functions that Oracle covered across various departments:
Implementation Strategy
The implementation strategy relied on an agile approach using the Scrum methodology to manage the Oracle implementation project. A comprehensive Project Plan was developed, outlining project phases, activities, and timelines. Each day, the team reviewed and updated this plan to maintain accurate tracking of project progress and priorities.
We divided the project into sprints, typically lasting a short duration like two weeks, to plan, execute, and review specific tasks. Through daily stand-ups, the team shared updates, identified obstacles, and adjusted the plan to accommodate emerging changes or challenges.
This methodology provided exceptional flexibility and immediate responsiveness as we progressed, enabling us to adapt to evolving needs and maximize execution efficiency. Additionally, it promoted transparency, continuous communication, and collaborative decision-making, facilitating team alignment and leading us to successfully achieve the objectives of the Oracle implementation project.
deliverables
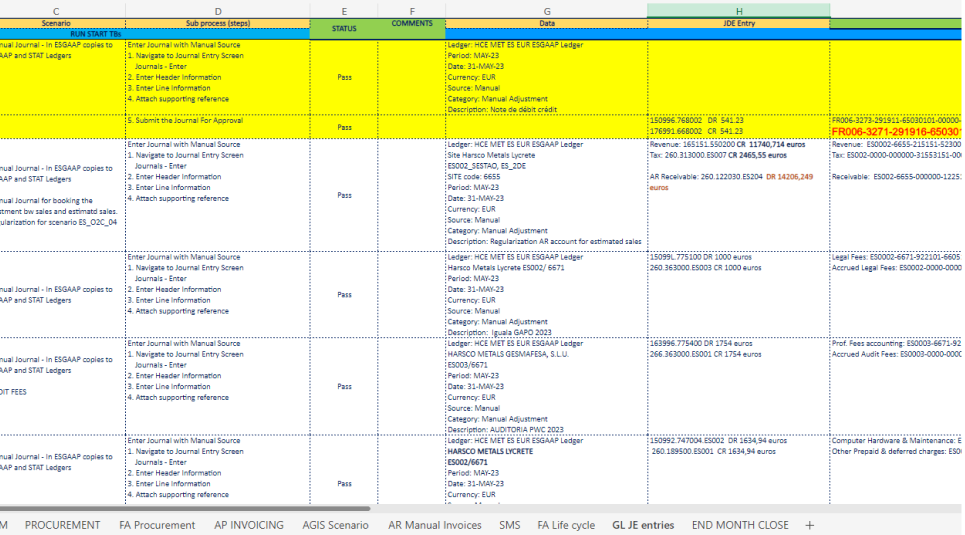
Prior to the official implementation, comprehensive testing was conducted at each key stage of the project, from design to deployment, aiming to identify, resolve, and validate potential issues or errors. At these stages, an ‘official sign-off’ was obtained before moving forward, ensuring all parties were informed about the project’s progress and had the opportunity to thoroughly review and approve the work conducted. This approval process ensured full alignment and informed decision-making at every crucial phase of the project.
# User Acceptance Test
During the UAT (User Acceptance Testing), users tested the software to verify if it met their needs and expectations. This involved running test scenarios, checking functionality, usability, integration with other systems, and confirming that the software operated correctly in the intended operational context.
The primary goal of the UAT was to validate that the software met previously agreed-upon criteria and was ready for implementation in production. Findings and issues discovered were documented and addressed before the final delivery of the software to end-users.

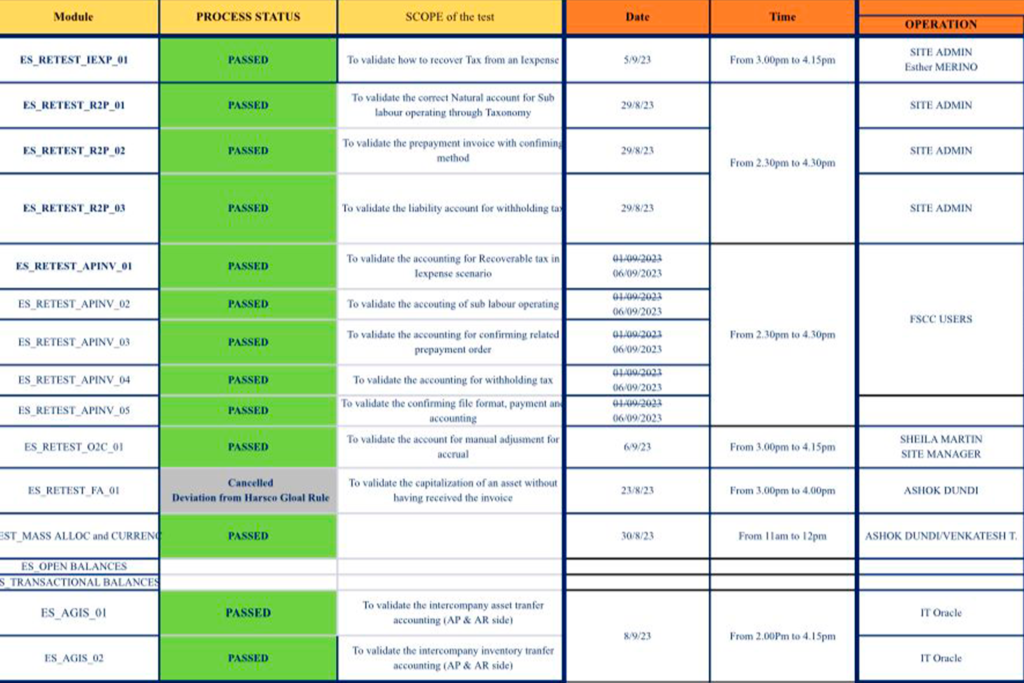
# UAT Retest
During the UAT session, errors were identified in certain aspects that required corrections. As a result, we organized a UAT Retest to ensure that the issues were effectively resolved.
# Training Material
Training material was developed applying fundamental principles of interface design and user experience. After a detailed analysis of training needs, crucial areas were identified based on users’ skills and knowledge. Emphasis on accessibility and content comprehension was achieved through a user-centered design, focusing on readability, visual clarity, and a logical structure. Visual consistency using a uniform palette of colors and styles strengthened the association of elements within the training materials.


# Training On Site & Online
Both in-person and online training sessions were implemented to ensure comprehensive training for all users, ensuring their ability to effectively use the software. In-person training allowed direct and hands-on interaction, offering the opportunity to address specific questions and resolve concerns in real-time. On the other hand, online sessions provided flexibility and remote access, facilitating continuous learning and prompt query resolution.
In addition to the initial training, follow-up online sessions were organized to provide ongoing support and address any queries that might arise during implementation or everyday use of the software. These sessions were crucial for reinforcing acquired knowledge, resolving specific issues, and keeping users updated on any relevant system updates or changes. This combination of in-person and online training ensured that all users were well-prepared and supported in using the software at all times.
Key Takeaways
The process of consolidating lessons learned began at an individual level, where each team member reflected on their experience in the project. During this phase, observations were documented regarding what worked well, areas that could have been improved, and recommendations for future actions.
Subsequently, in the collective phase, a joint session was conducted to review and share these lessons learned. During this meeting, patterns and common themes among individual experiences were identified, allowing for a more holistic understanding of challenges and successes. Corrective actions were prioritized, lessons were consolidated into a report, and action plans were developed to enhance performance in future country implementations.

Oracle EBS Implementation
the project

Oracle Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) offers solutions for enterprise resource planning, aiding organizations in managing their financial operations, supply chains, and other key aspects in an integrated manner.
Scope: Implementing Oracle across workplaces in Spain and Portugal, covering critical areas for the company’s functioning such as Procurement, Finance, Sales, Purchase Order Generation, and Receipt. The goal was to enhance operational efficiency, system integration, and optimize business processes.
Key stakeholders
The software implementation took place simultaneously across all organization workplaces, encompassing locations in Huelva, Barcelona, Sestao, Reinosa, and Asturias. Although there are approximately 350 employees in Spain, around 40 were direct users of the software.
Here are the key functions that Oracle covered across various departments:
Finance
Optimization of economic data management, enhancing accounting, invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting. Oracle enabled greater control over income and expenses, more effective financial planning, and informed decision-making.
Buyers
Enhancement of procurement management, allowing more effective tracking of suppliers, orders, price comparison, and inventory management.
Site Managers
Oracle played a pivotal role in enhancing sales management, order tracking, and work order generation, thereby achieving greater operational efficiency at workplaces and significantly reducing delays and issues in the supply chain.
Site Admins
Oracle streamlined order management, inventory, and transaction coordination, ensuring smooth logistical flow and efficient coordination among departments.
project Phases
The project was structured into seven key phases spanning from inception to full operability and support. These phases represented pivotal milestones in the effective integration of Oracle’s enterprise solution. Each stage delineated a path starting from initial planning and culminating in system implementation and ongoing maintenance. Within each phase, specific activities took place, ranging from assessment and design to data migration, configuration, thorough testing, and the final transition to the operational environment.
The following slides provide a detailed visual representation of each stage, offering a clear and comprehensive understanding of the implementation process.

Core team
The project involved a core team comprising Oracle experts, project leaders, finance and procurement specialists, system analysts, and interface and translation consultants. This multidisciplinary team collaborated closely to ensure the successful implementation of Oracle across the five workplaces in Spain, contributing crucial technical and operational insights for each phase of the project.

Project Manager
Responsible for coordinating, planning, and overseeing all project phases to ensure timely delivery within agreed-upon limits of time, budget, and requirements. Collaborates closely with experts, manages resources, and facilitates change management and end-user training.

Program Manager
Focused efforts on overseeing and coordinating multiple simultaneous Oracle implementation projects. Managed alignment of goals, resources, and strategies across projects, ensuring successful execution and a global vision.

Business Relationship
Bridge between business areas and technology. Involved in aligning technological solutions with business objectives and requirements, collaborating closely with internal teams to identify improvement opportunities and deliver effective solutions that drive business growth and efficiency.

Programmer analyst
Oversaw the development, implementation, and maintenance of technological solutions, including data mapping creation to ensure effective system integration.

Functional Analyst
Understanding business needs and translating them into functional requirements for computer systems. Responsible for analyzing business processes, collaborating with end-users to understand their needs, and designing technological solutions.

Operations and Strategy Officer
Responsible for overseeing strategic and tactical execution, delegating responsibilities, and supervising solution implementation. Additionally, involves a comprehensive understanding of organizational data, finances, and processes
Implementation Strategy
Scrum Metodology
The implementation strategy relied on an agile approach using the Scrum methodology to manage the Oracle implementation project. A comprehensive Project Plan was developed, outlining project phases, activities, and timelines. Each day, the team reviewed and updated this plan to maintain accurate tracking of project progress and priorities.
We divided the project into sprints, typically lasting a short duration like two weeks, to plan, execute, and review specific tasks. Through daily stand-ups, the team shared updates, identified obstacles, and adjusted the plan to accommodate emerging changes or challenges.
This methodology provided exceptional flexibility and immediate responsiveness as we progressed, enabling us to adapt to evolving needs and maximize execution efficiency. Additionally, it promoted transparency, continuous communication, and collaborative decision-making, facilitating team alignment and leading us to successfully achieve the objectives of the Oracle implementation project.

Project Plan
Deliverables
Prior to the official implementation, comprehensive testing was conducted at each key stage of the project, from design to deployment, aiming to identify, resolve, and validate potential issues or errors. At these stages, an ‘official sign-off’ was obtained before moving forward, ensuring all parties were informed about the project’s progress and had the opportunity to thoroughly review and approve the work conducted. This approval process ensured full alignment and informed decision-making at every crucial phase of the project.
User Acceptance Test (UAT)
During the UAT (User Acceptance Testing), users tested the software to verify if it met their needs and expectations. This involved running test scenarios, checking functionality, usability, integration with other systems, and confirming that the software operated correctly in the intended operational context.
The primary goal of the UAT was to validate that the software met previously agreed-upon criteria and was ready for implementation in production. Findings and issues discovered were documented and addressed before the final delivery of the software to end-users.


UAT Scenarios
UAT Results
UAT Retest
During the UAT session, errors were identified in certain aspects that required corrections. As a result, we organized a UAT Retest to ensure that the issues were effectively resolved.


UAT retest
Training Material
Training material was developed applying fundamental principles of interface design and user experience. After a detailed analysis of training needs, crucial areas were identified based on users’ skills and knowledge. Emphasis on accessibility and content comprehension was achieved through a user-centered design, focusing on readability, visual clarity, and a logical structure. Visual consistency using a uniform palette of colors and styles strengthened the association of elements within the training materials.


Training On Site & Online
Both in-person and online training sessions were implemented to ensure comprehensive training for all users, ensuring their ability to effectively use the software. In-person training allowed direct and hands-on interaction, offering the opportunity to address specific questions and resolve concerns in real-time. On the other hand, online sessions provided flexibility and remote access, facilitating continuous learning and prompt query resolution.
In addition to the initial training, follow-up online sessions were organized to provide ongoing support and address any queries that might arise during implementation or everyday use of the software. These sessions were crucial for reinforcing acquired knowledge, resolving specific issues, and keeping users updated on any relevant system updates or changes. This combination of in-person and online training ensured that all users were well-prepared and supported in using the software at all times.
Lessons learnt
The process of consolidating lessons learned began at an individual level, where each team member reflected on their experience in the project. During this phase, observations were documented regarding what worked well, areas that could have been improved, and recommendations for future actions.
Subsequently, in the collective phase, a joint session was conducted to review and share these lessons learned. During this meeting, patterns and common themes among individual experiences were identified, allowing for a more holistic understanding of challenges and successes. Corrective actions were prioritized, lessons were consolidated into a report, and action plans were developed to enhance performance in future country implementations.
👍 What went well?
- Utilization of training guides and effective in-person sessions.
- The pre-launch training sessions at the centers were beneficial for user readines.
✍️ What could have been done better?
- Define scenarios more precisely for AP/AR/Sales practical sessions.
- The AP training sessions would have been more effective if the trainer had possessed accounting knowledge in addition to technical skills, as users raised questions that couldn’t be immediately resolved, impacting the training effectiveness.
🎓 What should have been done differently?
- Reducing unnecessary repetitive sessions and prioritizing intensive, high-quality training sessions.
- Better preparedness of the training instance to closely align with the production setup would have enhanced training effectiveness.
👍 What Went Well?
- The cohesive working model among Oracle, MDM, and FSSC ensured seamless and effective integration between key systems.
- Planning was facilitated by valuable past experiences in Oracle implementations, enabling a more robust and focused strategy.
✍️ What Could Have Been Done Better?
- During the CRP sessions, incomplete mapping and lack of communication about changes were identified, areas that could have been improved for a smoother transition.
- Enhancing communication between the business and IT departments could have fostered greater collaboration and mutual understanding.
🎓 What Should Have Been Done Differently?
- It would have been beneficial to address mapping issues continuously, ensuring their correction throughout the process.
- Reducing unnecessary meetings and focusing on communication quality would have allowed for more efficient and effective interaction among teams.
👍 What Went Well?
- Validation of data loaded in production, ensuring system integrity and accuracy.
- Active involvement of the finance department during implementation, providing key insights and collaborating effectively
✍️ What Could Have Been Done Better?
- The lack of credit limit verification post-data migration could have been improved to ensure a smoother transition.
- The MDM department didn’t adequately control or verify supplier data, an area that could have been focused on with more detail.
🎓 What Should Have Been Done Differently?
- Greater control and review of Oracle data would have prevented significant variations and ensured optimal coherence in the system.
- Increased involvement of the PowerBI team in discussions regarding center name changes would have enriched strategic decisions and their implementation.
👍 What Went Well?
- The successful choice of Arin as a partner for integrating the Ticket Bai system ensured a successful implementation.
- A highly collaborative remote team that effectively worked across different geographical locations
✍️ What Could Have Been Done Better?
- Improving system monitoring to identify unreceived emails and ‘Failed’ approval statuses would optimize communication processes.
- Earlier task planning by resources would have been beneficial to streamline activity execution.
🎓 What Should Have Been Done Differently?
- To further optimize resource allocation for key activities like end-of-month simulations and training sessions, maximizing their effectiveness.
- Increased involvement of Procurement users in training local buyers would have strengthened the adaptation to the new system.